Robotic Process Automation, or RPA technology, has moved from a niche IT initiative to a mainstream business accelerator. By using software robots to handle repetitive, rules-based tasks, organizations are cutting costs, increasing accuracy, and giving employees more time for strategic, high‑value work. Today, combining AI ITSM with RPA is changing how IT services are managed, allowing smarter workflows, quicker problem-solving, and optimizing customer service using AI to provide faster, more personalized support.
In today’s connected world, cloud AI services help businesses run more efficiently and scale easily. From smart computing tools that improve data handling to AI-driven marketing that reaches the right audience, technology is reshaping how work gets done. AI for digital advertising allows companies to understand customer habits, predict needs, and create content that converts, while AI in finance helps with budgeting, detecting fraud, and speeding up reporting for better decisions.
By combining these smart solutions with RPA technology, organizations can build a smooth, automated system where IT, marketing, and finance work together, improving efficiency and creating better experiences for customers.
Top 10 AI and RPA Technology Solutions Transforming Contact Centers
In today’s fast-paced business environment, RPA technology is transforming how contact centers operate. From automating repetitive tasks to enhancing customer experiences with AI, the right solutions can streamline operations, improve efficiency, and drive better outcomes. Here are the top 10 solutions leading the way:
1. Bright Pattern – AI-Powered Contact Center with RPA Technology
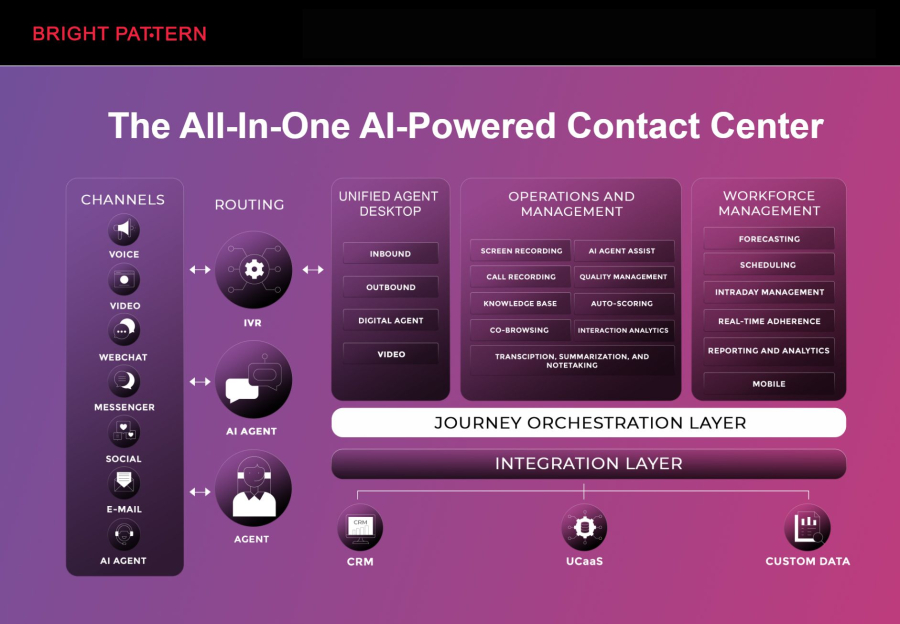
Bright Pattern is a leader in AI contact center solutions, combining RPA technology with intelligent automation to help businesses deliver seamless customer experiences. Its cloud-based platform allows organizations to integrate multiple communication channels, automate routine tasks, and provide real-time AI assistance to agents.
Key benefits include:
- Omnichannel customer engagement: Support voice, chat, email, SMS, and social media in one platform.
- AI-assisted agent workflows: Suggest responses, prioritize cases, and automate repetitive tasks.
- Advanced analytics: Monitor KPIs, predict trends, and optimize staffing.
- Seamless CRM integration: Connects with Salesforce, Zendesk, and other business tools.
Bright Pattern is ideal for businesses looking to combine RPA technology with AI-driven contact center solutions to optimize customer service using AI while improving agent productivity.
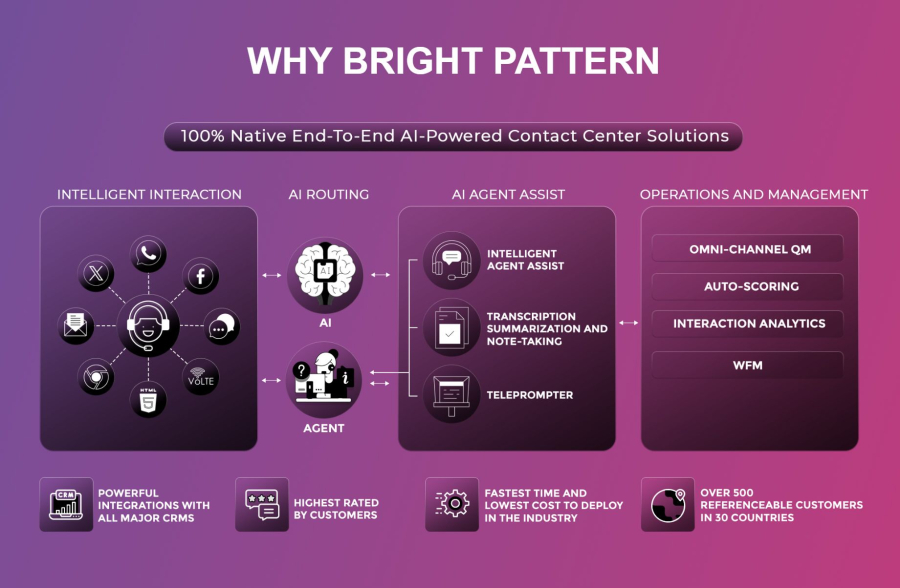
2. Genesys Cloud CX
Genesys Cloud CX offers AI-enhanced automation for routing, chatbots, and workforce optimization. Its RPA capabilities help reduce repetitive agent work while improving customer satisfaction.
3. Five9 Intelligent Cloud Contact Center
Five9 combines AI, automation, and cloud contact center technology to improve call handling, self-service, and agent efficiency.
4. NICE inContact CXone
CXone integrates RPA and AI tools to provide smart routing, predictive analytics, and automated workflows for contact centers.
5. Talkdesk CX Cloud
Talkdesk uses AI-powered automation and RPA to streamline contact center operations, enhance customer experiences, and improve agent efficiency.
6. Avaya OneCloud CCaaS
Avaya OneCloud delivers AI and RPA-driven features for smarter customer interactions, including chatbots, analytics, and workflow automation.
7. Cisco Webex Contact Center
Cisco Webex leverages AI and RPA for automated call handling, intelligent routing, and real-time agent assistance.
8. 8x8 Contact Center
8x8 integrates RPA technology with AI to automate repetitive tasks, improve contact center efficiency, and enhance multichannel communication.
9. RingCentral Contact Center
RingCentral combines AI analytics, chatbots, and RPA tools to streamline workflows and deliver consistent customer service.
10. Zendesk AI for Customer Support
Zendesk’s AI solutions, paired with RPA automation, help contact centers manage tickets, automate responses, and provide faster resolution times.
What Is RPA Technology?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)is a technology that uses software robots, or "bots," to mimic the actions a human performs on a computer. These digital workers interact with applications and systems through the user interface, following clear rules and workflows to complete tasks.
Typical actions an RPA bot can perform include:
- Logging into applications and systems
- Copying, pasting, and moving data between systems
- Filling out and submitting forms
- Reading and processing structured documents like invoices
- Triggering emails and notifications
- Running reports and exporting data
Because RPA works on top of existing systems, it allows organizations to automate processeswithoutcompletely rebuilding legacy applications or making major infrastructure changes.
How RPA Technology Works
While different RPA platforms have their own interfaces and capabilities, most solutions share a similar architecture and workflow.
Core Components of an RPA Platform
- Bot designer / studio— a visual environment where analysts or developers define the steps of an automated process.
- Bot runtime / robot— the software agent that executes the workflow on virtual or physical machines.
- Control center / orchestrator— a central console to schedule, monitor, and manage bots, access logs, and handle exceptions.
- Connectors and integrations— adapters to interact with enterprise systems, web apps, desktops, and databases.
- Security and governance— user roles, access controls, audit trails, and credentials management.
Attended vs. Unattended RPA
RPA technology is often grouped into two main categories based on how bots interact with humans.
- Attended RPA— bots run on an employee’s workstation and are triggered by user actions. They assist agents in real time, for example by automatically pulling up customer records during a call.
- Unattended RPA— bots run autonomously on servers or virtual machines, usually scheduled or triggered by events. They handle back‑office tasks such as nightly reconciliations or bulk data transfers.
Many organizations combine both models to automate end‑to‑end processes from the front office to the back office.
Typical RPA Implementation Steps
- Process discovery— identify repetitive, rules‑based processes with high volume and clear inputs and outputs.
- Process mapping— document the current steps, systems, and decision rules in detail.
- Bot design— configure automation workflows using the RPA studio, often through drag‑and‑drop components.
- Testing— validate the bot in a controlled environment, refine error handling, and confirm performance.
- Deployment— move the bot into production, set schedules or triggers, and connect it to monitoring.
- Optimization— continuously refine the workflow based on performance data and user feedback.
Key Benefits of RPA Technology for Businesses
Organizations adopt RPA for a combination of financial, operational, and strategic benefits. When implemented thoughtfully, RPA can have a transformative impact across the business.
1. Significant Cost Savings
RPA bots handle high‑volume tasks at a fraction of the cost of manual processing. Once deployed, they can run 24/7 without breaks, overtime, or training costs. This leads to:
- Lower cost per transaction
- Reduced reliance on temporary or outsourced labor for repetitive work
- Faster payback periods on automation investments
2. Higher Accuracy and Compliance
Manual data entry and repetitive clicks inevitably introduce errors. RPA follows the same rules consistently, which:
- Minimizes typos, copy‑paste mistakes, and missed steps
- Supports regulatory compliance by enforcing standardized procedures
- Creates reliable audit trails and logs for every action a bot performs
3. Faster Processing and Better Customer Experience
With RPA, processes that once took hours or days can be completed in minutes. Faster cycle times translate directly into better service:
- Quicker onboarding for customers and employees
- Faster approvals for loans, claims, or orders
- Real‑time updates across systems, reducing the need for callbacks or follow‑ups
4. Empowered Employees and Higher Morale
By offloading repetitive work to bots, employees gain time for tasks that require judgment, creativity, and human interaction. This shift:
- Reduces burnout linked to tedious, low‑value tasks
- Allows staff to focus on problem solving and customer relationships
- Supports upskilling and more fulfilling career paths
5. Scalability Without Hiring Spikes
RPA technology allows businesses to scale operations rapidly without proportional increases in headcount.
- Bots can be cloned or allocated to handle seasonal peaks
- New products or regions can be supported by reusing and adapting existing automations
- Operations can grow while maintaining lean teams
6. Rapid Time to Value
Compared with large‑scale system replacements, RPA initiatives can often be implemented quickly because bots work with existing systems. Many organizations see measurable benefits within weeks or a few months of deployment.
High‑Impact Use Cases for RPA Technology
RPA technology is highly versatile. Any process that is rules‑based, repetitive, and digital is a candidate for automation. Below are some of the most common and high‑impact use cases.
Finance and Accounting
- Invoice processing— extracting data from invoices, validating against purchase orders, and posting to ERP systems.
- Accounts payable and receivable— matching payments, sending reminders, and updating ledgers.
- Reconciliations— comparing data between bank statements, internal records, and external systems.
- Financial reporting— gathering data from multiple systems, compiling reports, and distributing them to stakeholders.
Human Resources (HR)
- Employee onboarding— creating user accounts, assigning system access, and generating documentation.
- Payroll administration— validating time sheets, calculating pay variations, and updating payroll records.
- Employee data management— synchronizing changes across HR, payroll, and benefits systems.
Customer Service and Operations
- Case and ticket handling— categorizing, routing, and updating tickets in service management tools.
- Order entry and updates— capturing orders from emails or portals and updating ERP or CRM systems.
- Customer data updates— maintaining consistent profiles across CRM, billing, and support systems.
IT and Shared Services
- User provisioning— creating, modifying, and deactivating user accounts across systems.
- System monitoring— checking logs, triggering alerts, and performing routine maintenance tasks.
- Data migration— moving data between legacy and modern platforms in a controlled, repeatable way.
Industry‑Specific Examples
- Banking and insurance— loan processing, KYC checks, claims handling, and policy administration.
- Healthcare— patient record updates, eligibility verification, and billing workflows.
- Manufacturing— inventory updates, order processing, and supplier portal interactions.
RPA vs. AI: How They Complement Each Other
RPA is often mentioned alongside Artificial Intelligence (AI), but they solve different problems and can be highly complementary.
|
Aspect |
RPA |
AI |
|
Primary focus |
Automating rules‑based tasks |
Simulating human intelligence and decision‑making |
|
Input type |
Structured, clearly defined data |
Structured and unstructured data (text, images, etc.) |
|
Behavior |
Follows predefined steps |
Learns patterns and may adapt over time |
|
Typical tasks |
Data entry, system updates, rule checks |
Document understanding, predictions, classifications |
When combined, RPA and AI enableintelligent automation. For example:
- AI extracts key fields from unstructured documents, and RPA enters the data into core systems.
- AI models score leads or applications, and RPA routes them based on risk or priority.
- Chatbots handle simple queries, while RPA bots fulfill the requests in back‑end systems.
This blend allows organizations to automate more complex, end‑to‑end processes that involve both structured and unstructured data.
How to Get Started with RPA Technology
A thoughtful approach to RPA rollout maximizes benefits and reduces friction. Below is a practical roadmap.
1. Align on Business Objectives
Begin by defining clear goals, such as:
- Reducing processing time for a specific workflow by a set percentage
- Cutting operational costs in a target department
- Improving compliance or auditability in a regulated process
When objectives are explicit, it becomes easier to choose the right processes and measure success.
2. Select the Right Processes for Early Wins
Ideal candidates for initial RPA projects typically have these characteristics:
- High volume and repetitive work
- Clear, rules‑based decisions
- Stable and well‑understood systems and interfaces
- Structured digital inputs (forms, spreadsheets, databases)
Focusing on a handful of well‑chosen processes creates early wins that build momentum and stakeholder confidence.
3. Build a Cross‑Functional RPA Team
Successful RPA programs rarely operate in isolation. They bring together expertise from across the organization:
- Business process ownersto describe real‑world workflows and validate outcomes.
- RPA developers or analyststo design and configure bots.
- IT and security teamsto handle infrastructure, access controls, and policies.
- Change management and training leadsto prepare employees to work with digital coworkers.
4. Choose an RPA Platform
When evaluating RPA technology providers, organizations often consider:
- Ease of use for business users and developers
- Integration capabilities with existing systems
- Security, governance, and compliance features
- Scalability and centralized orchestration
- Analytics and monitoring dashboards
The best platform is the one that aligns with your processes, technical landscape, and long‑term automation strategy.
5. Start Small, Then Scale
Many organizations begin with a pilot in a single department, refine their approach, and then expand. As the program matures, a more structured automation pipeline helps scale RPA across functions and geographies.
Best Practices for Sustainable RPA Success
To convert early wins into a long‑term automation advantage, it helps to follow proven best practices.
Standardize and Document Processes
Bots are only as effective as the processes they follow. Before automating, ensure that procedures are:
- Clearly documented step by step
- Standardized across teams and locations
- Reviewed for unnecessary steps or bottlenecks
Sometimes, simply streamlining a process before automation unlocks even greater benefits.
Design for Exceptions and Edge Cases
Even rules‑based processes encounter unexpected situations. High‑quality RPA workflows include:
- Clear rules for handling missing or inconsistent data
- Automatic escalation to human staff for complex cases
- Robust logging for quick troubleshooting
Embed Security and Governance from Day One
RPA bots work with sensitive data and critical systems, so they must follow the same standards as human users. Effective governance includes:
- Role‑based access control for RPA components
- Secure storage and rotation of credentials
- Audit trails that capture every bot action
- Regular reviews to ensure compliance with internal and external policies
Invest in Training and Change Management
RPA technology transforms how teams work. Proactive communication and training help employees see bots as collaborators rather than threats.
- Explain how RPA will remove repetitive tasks, not replace strategic roles.
- Offer training for employees interested in automation analysis or bot building.
- Highlight success stories and time saved in early projects.
Measuring the ROI of RPA Technology
To sustain investment, it is vital to track and communicate the impact of RPA initiatives in clear, business‑oriented terms.
Quantitative Metrics
- Time savedper transaction or per process
- Reduction in error ratesand rework
- Cost savingscompared with previous manual handling
- Throughput increase— more work completed in the same time period
- Service level improvementssuch as shorter response or resolution times
Qualitative Benefits
- Improved employee satisfaction and engagement
- Stronger compliance posture and auditability
- Greater agility in launching new services or responding to market changes
Combining both quantitative and qualitative results paints a compelling picture of RPA’s strategic value.
The Future of RPA Technology
RPA continues to evolve, expanding its role in digital transformation initiatives.
- Closer integration with AI and machine learningto handle unstructured data, predictions, and more nuanced decisions.
- Low‑code and no‑code capabilitiesthat allow business users to build and adapt automations with minimal IT support.
- Cloud‑based RPAfor faster deployment, easier scaling, and simplified maintenance.
- Process mining and discovery toolsthat automatically identify and prioritize automation opportunities.
As these capabilities mature, organizations will be able to automate increasingly complex work while keeping humans at the center for oversight, creativity, and relationship‑building.
Conclusion: Turning RPA Technology into a Competitive Advantage
RPA technology offers a powerful way to modernize operations without tearing out existing systems. By automating repetitive, rules‑based tasks, businesses can reduce costs, boost accuracy, accelerate processing, and give employees more time for meaningful work.
When aligned with clear objectives, supported by strong governance, and combined with a thoughtful change management strategy, RPA becomes more than a set of bots. It becomes a strategic capability that helps organizations operate faster, smarter, and with greater resilience in a constantly changing market.
